World Diabetes Day 2022
Ms. Jaya (name changed) works in a shoe company in Vellore. The 36-year-old lives with her mother and two siblings. Her father passed away when she was very young. Her mother worked as a housemaid to provide for the family. Jaya never married and she supported her mother financially.
In 2017, Jaya had blisters on her left foot. When she showed it in CMC Vellore, she was diagnosed with Diabetes Mellitus. Because of her high sugar level, the wounds were infected and it did not heal. Her foot had to be partially amputated.
Jaya could not go back to work and this affected the family financially. She did not go back to CMC for follow ups. Over time, her blood sugar levels kept rising uncontrolled and her foot ulcer got worse without medical care.
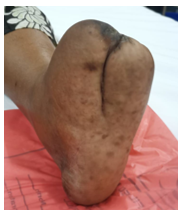
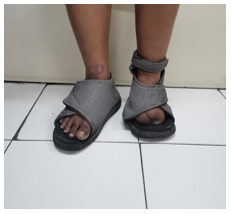
Since Jaya did not come back to see the doctor, the Department of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism reached out to help. The team knew that Jaya and her family were struggling financially. They gave her appropriate foot wear, mobility aids, glucometer with strips and medications. Encouraged by the Department’s support, Jaya became more regular for her checkups at the Integrated Diabetes Foot Clinic. The Clinic runs in association with PMR, Orthotics & Prosthetics, Surgery-I, Vascular Surgery and Plastic surgery. Here Jaya was trained on foot care and eventually the ulcer on her foot healed.
Now Jaya is back on her feet and is grateful for the Department’s support and care. The video below shows how the Endocrinology team treats a patient like Jaya.
Access to Diabetes Education
Diabetes doubles the risk of an early death. 1 in 2 people with diabetes don’t know they have it. Learn more about diabetes today
What is Diabetes?
Normally the pancreas produces insulin (a hormone) to control your blood sugar levels. When the body cannot make or effectively use insulin, your blood sugar builds up. This is diabetes. You may experience increased thirst, increased hunger and increased frequency of urination. Excess blood sugar can damage your blood vessels. This can have long-term effects on your body leading to complications like heart disease, kidney failure, stroke and nerve damage. Poor blood circulation can lead to amputation of a limb. Eye damage may lead to blindness.
Who can get diabetes?
Anyone can get diabetes. But your risk is higher if you are:
- Over 35 years of age
- Overweight
- Have a close family member with diabetes
Types of Diabetes
Type 1 (Juvenile diabetes) usually occurs in children or young adults.
You will need insulin every day.
Type 2 (Diabetes Mellitus) is much more
common – over 90% of cases.
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy
What do I do to avoid getting it?
- Do you know your weight and height? Click here to calculate your BMI (Body Mass Index) Maintain normal body weight
- Eat a healthy and balanced diet
- Exercise regularly – play games (no, not on your mobile phone!)
- Avoid drinking and smoking
What do I do if I get it?
If you are diabetic, don’t worry: you can live a normal life. Visit your doctor and get their medical advice. Follow the mantra of FAMM (food-activity-monitoring-medication) and protect your FAMily!
- Manage your diet
- Get active
- Monitor your blood sugar
- Take regular medication
Prasad* is a bright 29-year-old entrepreneur. For the last 20 years he has been living with diabetes.
“I was only 9 years old when I was diagnosed with Type I Diabetes. My family and friends are my biggest support. For the last 20 years, CMC Hospital has been a big part of my life as a juvenile diabetic.”
Prasad is disciplined in keeping his diabetes under control. He manages his diet and exercises daily to keep his weight in check. He checks his blood sugar level every day and takes his medications. regularly. He has found support from the WhatsApp group set up by CMC’s Department of Endocrinology.
“Interacting with others patients who face similar challenges reminds me I am not alone in this journey. We are all learning how to live normally with diabetes.”
Prasad is an inspiration to other young people with diabetes.
*Names changed
What’s on your plate?

Is your family eating a healthy diet?
A well balanced Indian diet includes:
- Cereals (rice, wheat, ragi, corn, pearl millet, sorgum)
- Dhal & Vegetables
- Milk &/or Meat &/or nuts
- Fresh seasonal fruits
Our Department of Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism cares for around 2,000 people with diabetes each month.
Visit our website for wellness diet charts
(Tamil, Telegu, Hindi & English)


